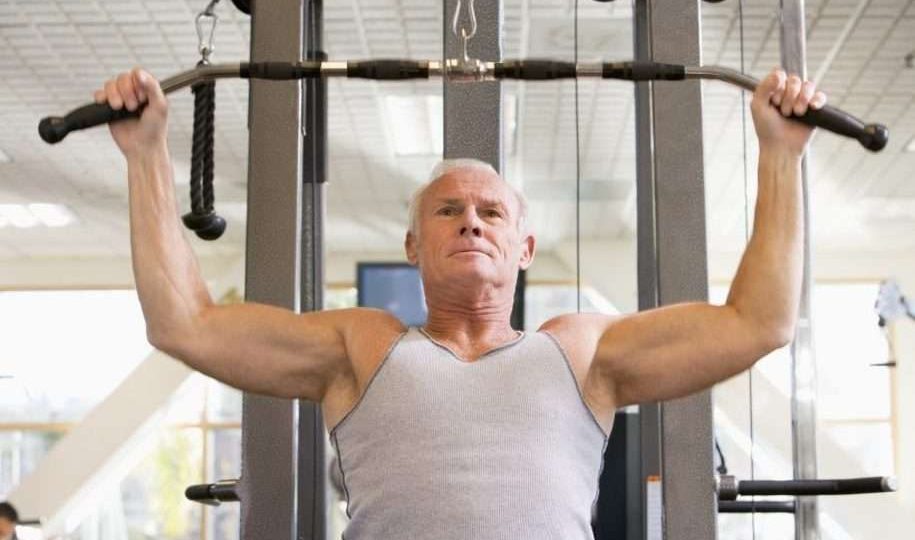
As we age, it is important to prioritize strength training to maintain muscle mass, bone density, and overall physical function. Engaging in regular strength training exercises can help prevent age-related decline, improve balance, reduce the risk of falls, and enhance overall quality of life. In this article, we will explore the benefits of strength training for older adults and provide some effective exercises to incorporate into your routine.
Benefits of Strength Training for Older Adults
1. Prevention of Muscle Loss: Aging is often associated with muscle loss or sarcopenia. Strength training helps counteract this process by building and maintaining muscle mass. This not only improves overall strength but also enhances metabolism and helps in maintaining a healthy weight.
2. Bone Health Improvement: As we age, the risk of osteoporosis and bone fractures increases. Strength training exercises that involve weight-bearing movements and resistance can stimulate bone growth, improve bone density, and reduce the risk of fractures.
3. Enhanced Balance and Stability: Strength training exercises that focus on core strength and stability can significantly improve balance and reduce the risk of falls, which is a major concern for older adults. This leads to improved mobility and independence in daily activities.
4. Chronic Disease Prevention: Regular strength training has been shown to help prevent chronic conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and arthritis. It can lower blood pressure, improve blood sugar control, and reduce joint pain and stiffness, thus improving overall health and well-being.
Effective Strength Training Exercises for Older Adults
1. Squats: Squats are a great compound exercise that targets multiple muscle groups, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and core. Start by standing with your feet shoulder-width apart, then slowly lower yourself into a sitting position as if you are sitting back into a chair. Make sure to keep your knees aligned with your toes and return to the starting position. Repeat for a set of 10-15 repetitions.
2. Push-Ups: Push-ups are an effective upper body exercise that engages the chest, triceps, shoulders, and core muscles. Begin by assuming a plank position with your hands shoulder-width apart. Lower your body towards the floor, ensuring your elbows are at a 90-degree angle, and then push back up. Modify the exercise by performing push-ups against a wall or on an inclined surface if needed. Aim for 2-3 sets of 8-12 repetitions.
3. Planks: Planks strengthen the core and improve stability. Start by assuming a push-up position with your arms fully extended and directly beneath your shoulders. Maintain a straight line from your head to your heels, engaging your core throughout the exercise. Hold the position for 30-60 seconds, gradually increasing the duration as you become more comfortable.
4. Dumbbell Overhead Press: This exercise targets the shoulder muscles. Start by sitting on a chair with your back straight and a dumbbell in each hand. Raise the dumbbells until your arms are fully extended overhead and then lower them back down to shoulder level. Aim for 2-3 sets of 10-12 repetitions.
Conclusion
Incorporating strength training exercises into your routine as you age can have numerous benefits for your overall health and well-being. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional or a certified trainer before starting any new exercise program to ensure safety and accuracy in performing the exercises. Remember that consistency is key, and with regular strength training, you can stay strong, maintain your independence, and improve your quality of life as you age.